
China National Space Agency (CNSA) released the first group images of the Martian surface last Friday, taken by its rover Zhurong, who landed on Tuesday last month. State media hailed it as a sign of the "complete success" of the mission.
The space agency said in a statement that the high-resolution photos were unveiled during a special ceremony in Beijing, marking "the full success of China's first Martian exploration mission."

The Zhurong rover, named after a fire god in Chinese mythology, landed on Mars' Utopia Planitia region on May 15. Thus, China completed its first Mars mission.
With this mission, China made history as the second country to land an exploration vehicle on the planet Mars.
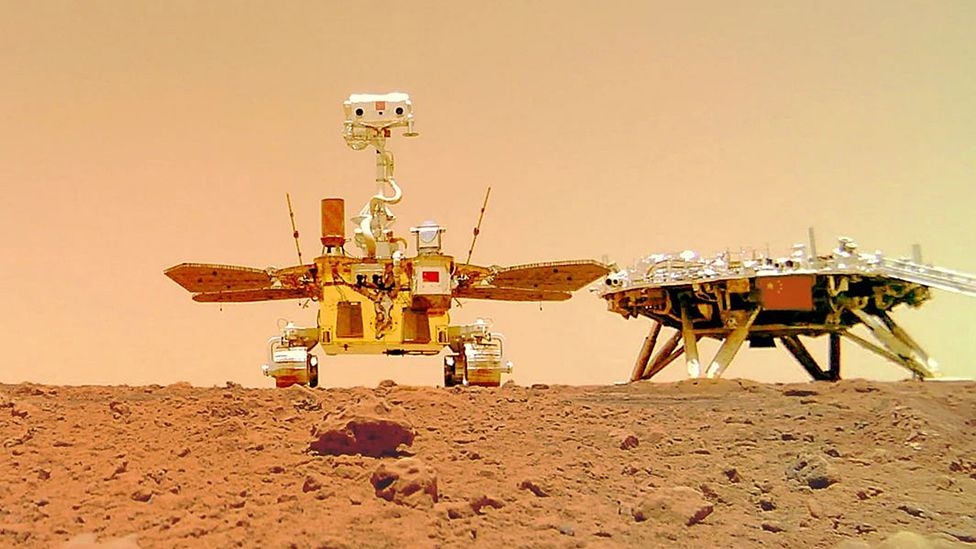
In one of the snapshots, the Zhurong rover and the mission's landing platform appear to carry the Chinese flag amid the planet's rocky and reddish terrain.
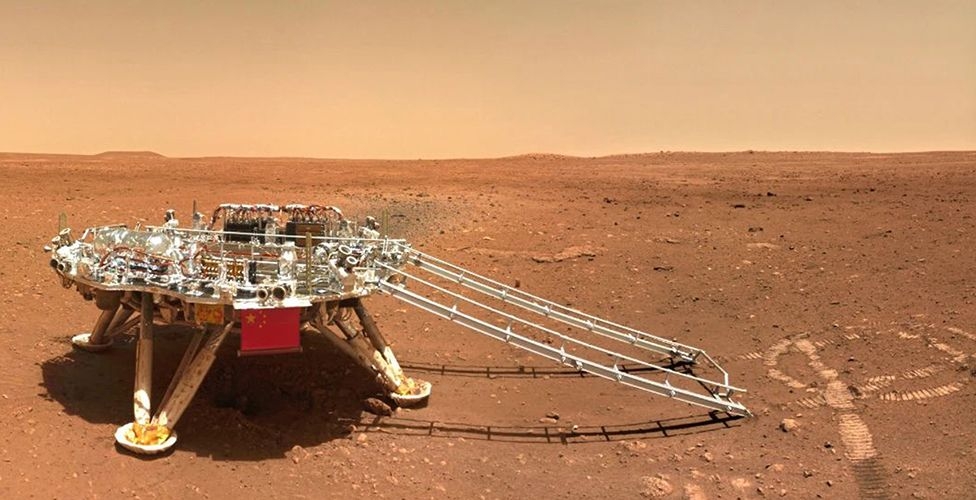

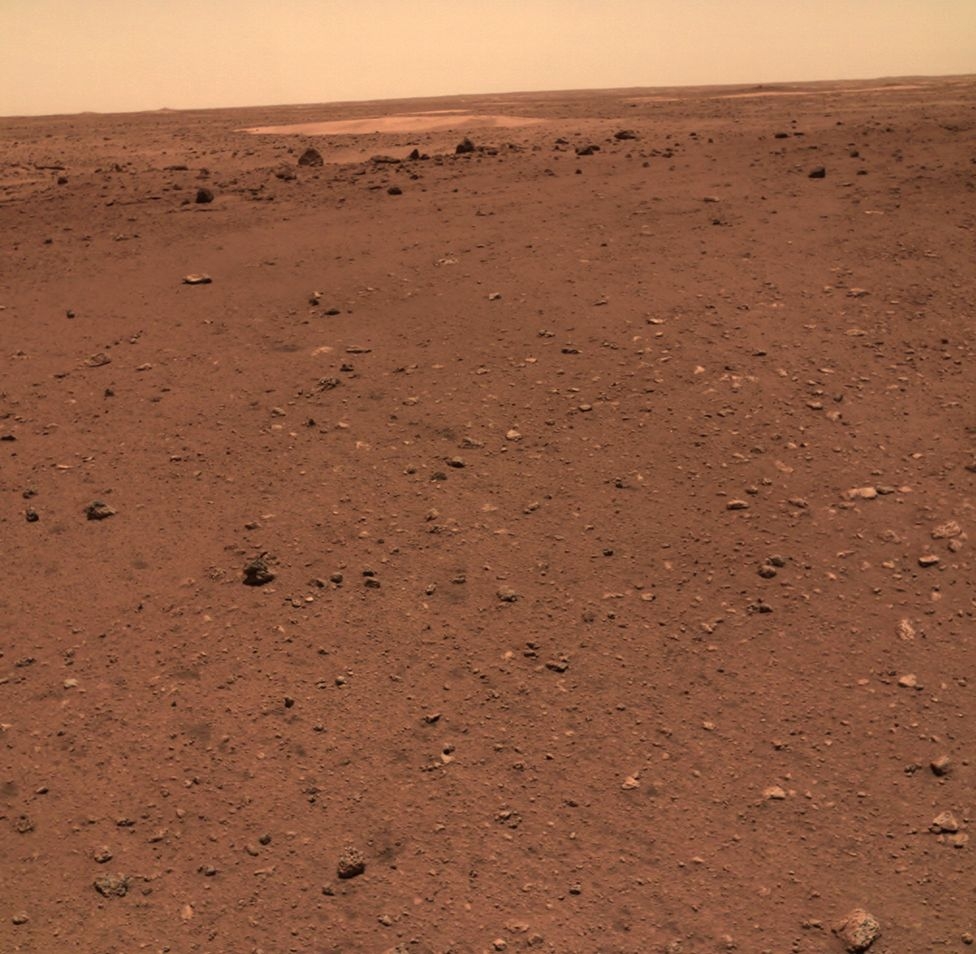
A panoramic view of the landing site taken with the rover camera shows that the surface of Mars in that area appears relatively flat with rocks scattered in varying sizes. Farther away you can even see some dunes.
In other photos, you can see some of the rover's components, such as the solar panels and communication systems that power it.
While Zhurong isn't as technologically advanced as NASA's Perseverance currently roaming Mars, its presence sends a clear message that China's space capabilities are catching up with those of the United States.

Chinese astronauts have long been excluded from the International Space Station, and this mission was one of the Chinese goals is to build its space station. In fact, the first module of the planned facility was successfully put into operation in April, one step closer to this goal.
The Tianwen-1 mission, consisting of an orbiter, a landing pad, and rover, was launched in July last year. The lander reached the red planet's surface on May 15 in the southern part of Utopia Planitia, a vast plain in the northern hemisphere.


The core module is currently the largest spacecraft developed by China. But the station will have to be assembled from several modules launched at different times; According to Chinese state media, the station could be fully operational by the end of 2022.